The Future of AI in the Construction Industry: A Blessing or a Burden?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly becoming a cornerstone of innovation across many industries, and construction is no exception. Traditionally resistant to major technological disruption, the construction industry is now beginning to embrace AI tools that promise to revolutionize how projects are designed, executed, and maintained. However, with these advancements come both opportunities and challenges. While AI has the potential to address many pain points within construction, it also raises concerns related to employment, cost, and risk.
In this blog, we’ll explore the future uses of AI in construction, how it can help improve efficiency and safety, and why its growing adoption could also create some unintended negative consequences.
How AI Will Shape the Future of Construction
AI technologies offer wide-ranging benefits in construction, with applications in areas such as design optimization, project planning, risk management, safety monitoring, and even autonomous machinery. Let’s take a closer look at some key ways AI can transform the industry.
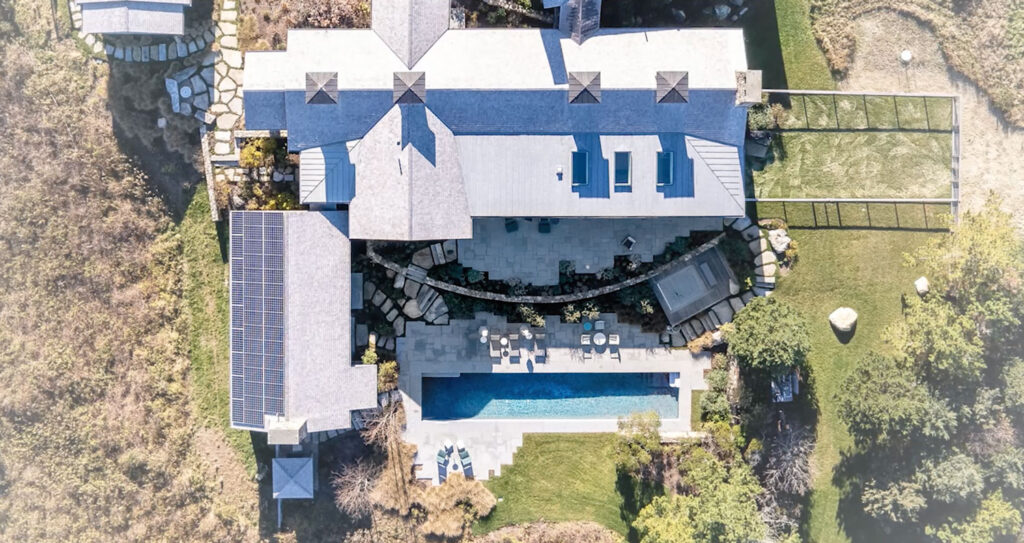

Improved Project Design and Planning
One of AI’s greatest strengths is data analysis. In construction, this capability allows AI-driven tools to analyze complex design parameters, local conditions, and historical data to optimize architectural plans and project schedules. Tools powered by AI can simulate different design options and automatically identify the most efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable approach.
For example, Building Information Modeling (BIM) software, enhanced with AI, can generate more accurate 3D models that include structural, mechanical, and environmental factors. These models can help architects and engineers avoid costly design errors and optimize material use before construction even begins.
Automation of Repetitive Tasks
AI is at the forefront of automating time-consuming and repetitive tasks in construction. For instance, AI-powered robots can handle tasks like bricklaying, concrete pouring, and welding with remarkable precision. This reduces labor costs and accelerates project timelines. Drones equipped with AI can survey construction sites, track progress, and provide real-time updates. They can monitor large sites more efficiently than human inspectors, minimizing delays and improving productivity.
Enhancing Worker Safety
Construction remains one of the most dangerous industries in the world. AI can play a critical role in improving worker safety by predicting risks and preventing accidents. AI-powered wearable devices can monitor workers’ vitals, fatigue levels, and location to detect signs of danger. Similarly, machine learning algorithms can analyze site data to identify potential hazards before they become serious threats.
For example, computer vision systems can analyze real-time camera footage to detect unsafe behavior, such as workers not wearing protective gear, and alert supervisors immediately. AI can also be used to forecast equipment failures, preventing costly and dangerous accidents.
Predictive Maintenance and Equipment Management
Heavy machinery is essential for large-scale construction projects but can be prone to breakdowns if not properly maintained. AI algorithms can analyze sensor data from equipment to predict when maintenance is required, helping prevent costly downtime. Predictive maintenance can increase the lifespan of construction assets and reduce the risk of unexpected failures.
Sustainability and Resource Optimization
Sustainability is becoming a key priority in construction as governments and developers push for greener infrastructure. AI can help reduce waste by optimizing resource allocation and material usage. Machine learning models can analyze supply chain data to minimize excess inventory, improve logistics, and reduce carbon footprints.
Additionally, AI can optimize energy consumption for construction processes and the operation of completed buildings. This leads to more sustainable projects with lower long-term costs for owners and developers.

How AI Could Hurt the Construction Industry
While AI offers a wealth of benefits, it is not without its downsides. Some concerns include job displacement, data security risks, and over-reliance on technology.
Job Displacement and Workforce Transformation
One of the most significant concerns surrounding AI in construction is its potential to displace workers. Tasks that were once labor-intensive, such as surveying, bricklaying, and inspection, are increasingly being performed by machines and software. While AI is unlikely to eliminate all construction jobs, it may reduce demand for certain roles, particularly those that involve repetitive or low-skill tasks.
However, AI may also create new opportunities in areas like AI system management, maintenance, and data analysis. The challenge lies in ensuring that workers are reskilled to take on these new roles.
Cybersecurity Risks
As construction sites become more reliant on interconnected systems, they also become more vulnerable to cyberattacks. Hackers could potentially disrupt operations by targeting AI-driven machinery, supply chain networks, or data systems. The construction industry may need to adopt stricter cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive information and infrastructure.
Over-Reliance on Technology
While AI can improve efficiency, over-reliance on technology may introduce new risks. For example, if AI systems malfunction or provide incorrect predictions, construction teams may face costly delays and errors. It is essential for human oversight to remain a critical component of AI implementation.
Ethical and Legal Challenges
The use of AI in construction raises ethical questions about worker privacy, safety, and accountability. For instance, if an AI system fails and causes an accident, who is responsible? The developer of the AI, the construction company, or the equipment operator? These legal and ethical challenges will require new regulatory frameworks to address the complexities of AI use.

Striking a Balance for the Future
The future of AI in construction is filled with promise but also fraught with challenges. To fully realize the potential benefits, industry leaders must take a balanced approach that includes investing in both technology and workforce development. By addressing concerns around job displacement, cybersecurity, and ethical risks, the construction sector can harness AI to build a safer, more efficient, and more sustainable future.
Ultimately, AI should be seen not as a replacement for human expertise but as a powerful tool to enhance it. With the right strategies in place, the construction industry can thrive in the age of artificial intelligence.
What are your thoughts on AI in construction? Are you optimistic about its potential, or do you have concerns about its impact? Share your insights in the comments below!